Linear relations among traits alfalfa cultivars
Palabras clave:
Medicago sativa L., Forage, Uniformity trial, CorrelationResumen
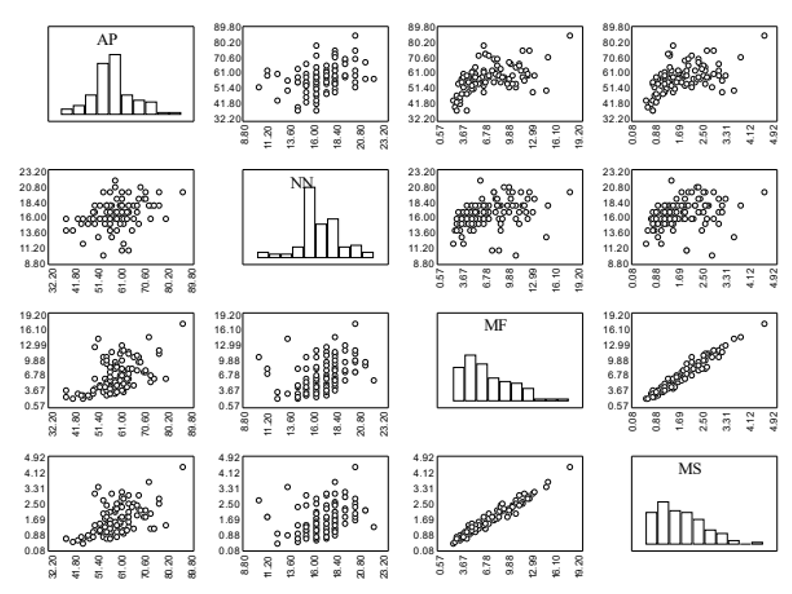
The objective of this work was to verify whether there are positive linear relations among traits of two alfalfa cultivars and which traits can be used for indirect selection. To this end, two uniformity trials were conducted, one with the Crioula cultivar and the other with the Trifecta cultivar, in Santa Maria, RS. Sowing was carried out manually on November 27, 2023. At flowering, 110 plants of each cultivar were randomly collected. In each plant, the traits evaluated were: plant height (PH), number of nodes (NN), fresh matter mass (FM) and dry matter mass (DM). For each cultivar, the matrix of Pearson's linear correlation coefficients (r) between the four traits was determined, with significance verified using Student's t test at 5%. The parameters of the regression tree algorithm were estimated to predicting FM and DM as a function of PH and NN. Among the traits of the Crioula cultivar, the r ranged from 0.30 (NN vs DM) to 0.97 (FM vs DM), with an average of 0.51. Among the traits of the Trifecta cultivar, the r ranged from 0.24 (NN vs FM) to 0.97 (FM vs DM) with an average of 0.51. There are positive linear relations between the traits plant height, number of nodes, fresh matter mass and dry matter mass, of the alfalfa cultivars Crioula and Trifecta. Plant height has positive linear relations with the fresh and dry matter masses of the aerial part and can be used for indirect selection.
Citas
ALLA, W. A. H et al. Evaluate of some varieties of alfalfa for forage yield and its components under the New Valley conditions. Journal of Agro Alimentary Processes and Technologies, v.19, n.4, p.413-418, 2013.
ALVARES, C. A. et al. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, v.22, n.6, p.711-728, 2013.
ARAB, S. A.; SHAL, M. H.; HAMED, N. M. Evaluation of some alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) germplasm for yield and yield component traits. Egyptian Journal of Agronomy, v.37, n.1, p.69-78, 2015.
ATUMO, T. T. et al. Adaptability, forage yield and nutritional quality of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) genotypes. Sustainable Environment, v.7, n.1, p.1-7, 2021.
AVCI, M. A.; OZKOSE, A.; TAMKOC, A. Determination of yield and quality characteristics of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) varieties grown in different locations. Journal of Animal and Veterinary Advances, v.12, n.4, p.487-490, 2013.
BUSSAB, W. O.; MORETTIN, P. A. Estatística Básica. São Paulo, 9. ed., n. 1, 2017.
CACAN, E.; KOKTEN, K.; KAPLAN, M. Determination of yield and quality characteristics of some alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars in the East Anatolia Region of Turkey and correlation analysis between these properties. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, v.16, n.2, p.1185-1198, 2018.
CARGNELUTTI FILHO, A. et al. Relações lineares entre caracteres de nabo forrageiro e de tremoço branco. Ciência Rural, v.44, n.1, p.18-24, 2014.
CARGNELUTTI FILHO, A. et al. Relações lineares entre caracteres de aveia preta. Ciência Rural, v.45, n.6, p.985-992, 2015.
DONMEZ, H. B.; HATIPOGLU, R. A research on the hay yield and quality of alfalfa cultivars with different fall dormancy rates under mediterranean climate conditions. Turkish Journal of Field Crops, v.28, n.2, p.194-202, 2023.
DUARTE, E. R. et al. Índice tecnológico na cultura de alfafa baseado na aplicação de fertilizantes em cobertura. Ensaios e Ciência, v.25, n.4, p.410-416, 2021.
FERREIRA, D. F. Estatística básica. 3. ed. Revisada e Ampliada. Lavras: UFLA, p. 624, 2018.
FERREIRA, R. P. et al. Cultivo e utilização da alfafa em pastejo para alimentação de vacas leiteiras. São Carlos: Embrapa Pecuária Sudeste, 2015.
FERREIRA, R. P. et al. Potencial forrageiro da alfafa para alimentação de vacas de leite nos trópicos. In: VILELA, D. (Ed.). Pecuária de leite no Brasil: cenários e avanços tecnológicos. São Carlos: Embrapa Pecuária Sudeste, p. 213-238, 2016.
GREVENIOTIS, V. et al. Modeling stability of alfalfa yield and main quality traits. Agriculture, v.14, n.4, p.1-17, 2024.
KONRAD, M. et al. Predição da massa fresca e massa seca da parte aérea da planta de teosinto em função de caracteres morfológicos. Sigmae, v.12, n.3, p.10-17, 2023.
LOH, W. Y. Classification and regression trees. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, v. 1, n. 1, p. 14-23, 2011.
MILBORROW, S. _rpart.plot: Plot ́rpart` Models: an Enhanced Version of ́plot.rpart`_. R package version 3.1.1, 2022. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rpart.plot.
OLOM, O. I. M.; WEI, Z.; NANA, L. Genetic diversity of the BC2 population of alfalfa multifoliate leaves based on morphological traits using correlation, principal component, and clustering analysis. The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, v.33, n.6, p.1346-1355, 2023.
ORTIZ, V. M. et al. Correlação e análise de trilha entre caracteres de teosinto. Sigmae, v.12, n.1, p.29-39, 2023.
R CORE TEAM. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, 2023. URL https://www.R-project.org/
RASSINI, J. B.; FERREIRA, R. P.; MOREIRA, A. Recomendações para o cultivo de alfafa na região Sudeste do Brasil. São Carlos: Embrapa Pecuária Sudeste, 2006. Circular Técnica.
REIS, M. B. et al. Árvore de regressão para previsão da produtividade de matéria fresca da parte aérea de teosinto em função de variáveis meteorológicas. Sigmae, v.12, n.3, p.24-31, 2023.
RODRÍGUEZ, E. N et al. Origem, disseminação, morfologia e fenologia. In: FERREIRA, R. P. et al. (Ed.). Alfafa: do cultivo aos múltiplos usos. Brasília: Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento, p. 21-41, 2020.
SANTOS, H. G. et al. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos. 5. ed. Brasília: Embrapa. p. 356, 2018.
THERNEAU, T.; ATKINSON, B. _rpart: Recursive Partitioning and Regression Trees_. R package version 4.1.19, 2022. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rpart.
TLAHIG, S. et al. Effect of cutting time on the performance of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) genotypes cropped in arid environment. Polish Journal of environmental studies, v.30, n.2, p.1817- 1829, 2021.
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Proposta de Política para Periódicos de Acesso Livre
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).
