Comparison of two classifiers in the identification of tree species based in continuous characters
Keywords:
Taxonomic problem, supervised learning, morphometrics, numeric taxonomy, multivariate normalAbstract
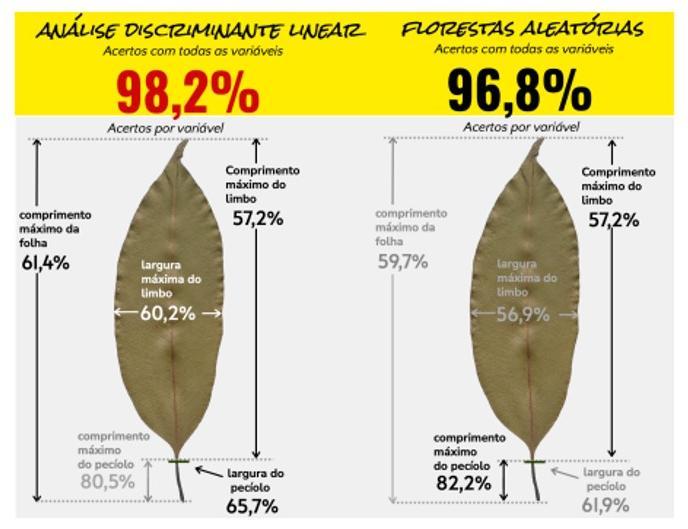
The species name assignment to a vegetable branch is the process called botanical identification and consists in a classification problem. The inclusion of continuous variables in this problem is not new, but it’s a growing topic. The objective of this paper was evaluate two classifiers that assign a specific name to a set of continuous measures of a leaf. There were collected 352 leaves from 5 species of Myrtaceae botanical family. There were measured 5 variables manually: maximum blade width, petiole width, leaf, blade and petiole maximum length. There were utilized two classifiers linear discriminant analysis (LDA) and random forests (RF). The data set was divided into train (70%) and test (30%) and 2000 iterations were conducted to each of 31 possible combination of variables. The models and classifiers were compared by the mean of the successful classification rate in the test set obtained in the 2000 iterations. As a result, considering all variable combinations, the LDA accuracy was 98.2% while the RF classified 96.8% correctly. The best isolated variable was the petiole maximum length and the best combination of two variables was the petiole maximum length and blade maximum width. LDA had a better performance than RF in the greater part of the variables combinations. These findings show the potential that this approach has to contribute as an aid to the botanical identification process.
References
BARRÉ, P. et al. Leafnet: A computer vision system for automatic plant species identification. Ecological Informatics, v. 40, p. 50–56, 2017.
COPE, J. S. et al. Plant species identification using digital morphometrics: A review. Expert Systems with Applications, v. 39, n. 8, p. 7562–7573, 2012.
DU, J.-X. et al. Computer-aided plant species identification (capsi) based on leaf shape matching technique. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, v. 28, n. 3, p. 275–285, 2006.
ELEN, A.; AVUÇLU, E. Automatic detection of petiole border in plant leaves. Measurement and Control, v. 54, n. 3-4, p. 446–456, 2021.
FISHER, R. A. The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Annals of Eugenics, Wiley Online Library, v. 7, n. 2, p. 179–188, 1936.
JOHNSON, R.; WICHERN, D. Applied multivariate statistical analysis. Pearson, 2014.
KUMAR, N. et al. Leafsnap: A computer vision system for automatic plant species identification. In: SPRINGER. Computer Vision–ECCV 2012: 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, October 7-13, 2012, Proceedings, Part II 12. [S.l.], 2012. p. 502–516.
LIAW, A.; WIENER, M. Classification and regression by randomforest. R News, v. 2, n. 3, p. 18–22, 2002. Disponível em: <https://CRAN.R-project.org/doc/Rnews/>.
LUNA-BONILLA, O. Á. D. et al. Leaf morphometric analysis and potential distribution modelling contribute to taxonomic differentiation in the quercus microphylla complex. Journal of Plant Research, v. 137, n. 1, p. 3–19, 2024.
LYSKO, A. et al. Comparison of discriminant methods and deep learning analysis in plant taxonomy: a case study of elatine. Nature, v. 12, n. 1, p. 20450, 2022.
MARKS, S.; DUNN, O. J. Discriminant functions when covariance matrices are unequal. Journal of the American Statistical Association, v.69, n. 346, p. 555–559, 1974.
MATTHEWS, G. J. et al. A comparison of machine learning techniques for taxonomic classification of teeth from the family bovidae. Journal of Applied Statistics, v. 45, n. 15, p. 2773–2787, 2018.
MURPHY, K. P. Probabilistic Machine Learning: An Introduction. [S.l.]: MIT press, 2022.
NASIR, A. F. A. et al. Automatic identification of ficus deltoidea jack (moraceae) varieties based on leaf. Modern Applied Science, v. 8, n. 5, p. 121, 2014.
OSO, O. A.; JAYEOLA, A. A. Digital morphometrics: Application of morpholeaf in shape visualization and species delimitation, using cucurbitaceae leaves as a model. Applications in Plant Sciences, v. 9, n. 9-10, p. e11448, 2021.
R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria, 2023. Disponível em: .
THANIKKAL, J. G.; DUBEY, A. K.; THOMAS, M. T. A novel edge detection method for medicinal plant’s leaf features extraction. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management}, v. 14, n. 1, p. 448–458, 2023.
VENABLES, W. N.; RIPLEY, B. D. Modern Applied Statistics with S. Fourth. New York: Springer, 2002. ISBN 0-387-95457-0. Disponível em: <https://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/pub/MASS4/>.
YIGIT, E. et al. A study on visual features of leaves in plant identification using artificial intelligence techniques. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, v. 156, p. 369–377, 2019.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Proposta de Política para Periódicos de Acesso Livre
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).
