Computacional tool to aid in the interpretation of laboratory tests
Keywords:
Laboratory analysis, Tool, Neural Networks, Tesseract, OCRAbstract
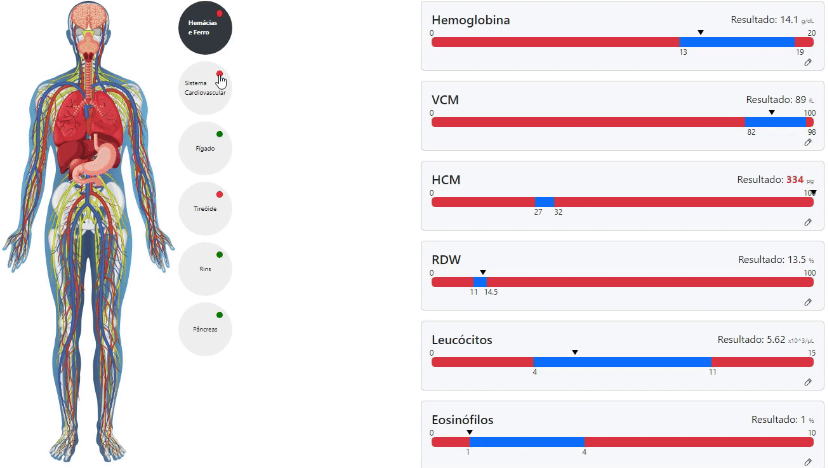
The interpretation of biochemical laboratory tests often presents significant challenges due to the diversity of formats and structures adopted by different laboratories. The variation in data presentation and lack of standardization often hinder the efficient analysis of these results, potentially leading to misinterpretation and imprecise diagnoses. Healthcare professionals face an obstacle when dealing with this heterogeneity, which can affect the quality and speed of the clinical decision-making process. In this context, this work focuses on developing an innovative tool to address this issue. An application was devised using advanced technologies such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR) combined with a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Recurrent Neural Network. This approach enables precise reading of tests from different laboratories, regardless of the formats used. The application stands out by creating an interface that standardizes the results in a way that simplifies the interpretation of the tests, thereby facilitating the diagnostic process for these professionals. The developed model represents an effective solution to the exposed problems, overcoming the complexity arising from the diversity of formats. By automating and simplifying the analysis, it contributes to reducing interpretation errors and, consequently, improving the quality of diagnoses, positively impacting efficiency and precision in the healthcare field.
References
AMBRÓSIO, Paulo Eduardo. Redes neurais artificiais no apoio ao diagnóstico diferencial de lesões intersticiais pulmonares. 2002. Tese de Doutorado. Universidade de São Paulo. Disponível em: https://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/59/59135/tde-26102002-155559/publico/Dissertacao.pdf. Acesso em: 10 de Outubro de 2023.
ANDRIOLO, A., et al. (2018). Recomendações da sociedade brasileira de patologia clínica/medicina laboratorial (SBPC/ML): fatores pré-analíticos e interferentes em ensaios laboratorias. Editora Manole Ltda.
DE CASTRO, F. C. C.; DE CASTRO, M. C. F. Redes neurais artificiais. Porto Alegre, RS: Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul, 2001.
FATEMAN, Richard J. et al. Optical character recognition and parsing of typeset mathematics1. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, v. 7, n. 1, p. 2-15, 1996.
GEEKSFORGEEKS. Introduction to Recurrent Neural Network.18 de Maio de 2023. Disponível em: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-to-recurrent-neural-network/. Acesso em: 20 de Out. de 2023.
HAYKIN, Simon. Redes neurais: princípios e prática. Bookman Editora, 2001.
ICMC-USP. Redes Multi Layer Perceptron treinadas com BackPropagation. Disponível em: https://sites.icmc.usp.br/andre/research/neural/#cara. Acesso em: 12 de Out. de 2023.
KOVÁCS, Zsolt László. Redes neurais artificiais. Editora Livraria da Fisica, 2002.
LIMA-OLIVEIRA G, Volanski W, Lippi G, Picheth G, Guidi GC. Pre-analytical phase management: a review of the procedures from patient preparation to laboratory analysis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2017 May;77(3):153-163. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2017.1295317. Epub 2017 Mar 7. PMID: 28266238.
MCCULLOCH, Warren S.; PITTS, Walter. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. The bulletin of mathematical biophysics, v. 5, p. 115-133, 1943.
META, Platform. Inc. Menlo Park, Califórnia, Estados Unidos, 2004.
MITHE, Ravina; INDALKAR, Supriya; DIVEKAR, Nilam. Optical character recognition. International journal of recent technology and engineering (IJRTE), v. 2, n. 1, p. 72-75, 2013.
NAGY, George. At the Frontiers of OCR. Proceedings of the IEEE, v. 10, n. 7, Julho de 1992. Disponível em: https://sites.ecse.rpi.edu/~nagy/PDF_files/Nagy_ProcsIEEE92-Frontiers-0f-OCR.pdf. Acesso em: 15 de Out. de 2023.
RAUBER, Thomas Walter. Redes neurais artificiais. Universidade Federal do Espírito Santo, v. 29, 2005. Disponível em: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Thomas-Rauber-2/publication/228686464_Redes_neurais_artificiais/links/02e7e521381602f2bd000000/Redes-neurais-artificiais.pdf. Acesso em: 16 de Out. de 2023.
SINGH, Amarjot; BACCHUWAR, Ketan; BHASIN, Akshay. A survey of OCR applications. International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing, v. 2, n. 3, p. 314, 2012. Disponível em: http://www.ijmlc.org/papers/137-L0022.pdf. Acesso em: 18 de Out. de 2023.
SOUSA, A. C. N.; RODRIGUES JUNIOR, O. M. . Main errors in the pre-analytical phase of laboratory tests: an integrative literature review. Research, Society and Development, [S. l.], v. 10, n. 15, p. e261101523662, 2021. DOI: 10.33448/rsd-v10i15.23662. Disponível em: https://rsdjournal.org/index.php/rsd/article/view/23662. Acesso em: 20 de Out. de 2023.
STAUDEMEYER, Ralf C.; MORRIS, Eric Rothstein. Understanding LSTM - a tutorial into Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Networks. 23 de Setembro de 2019. Disponível em: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.09586.pdf. Acesso em: 15 de Out. de 2023.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Proposta de Política para Periódicos de Acesso Livre
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).
