Nonlinear regression models as a tool to describe strawberry vegetative growth
Keywords:
Fragaria x ananassa Duch., Growth models, Albion, San AndreasAbstract
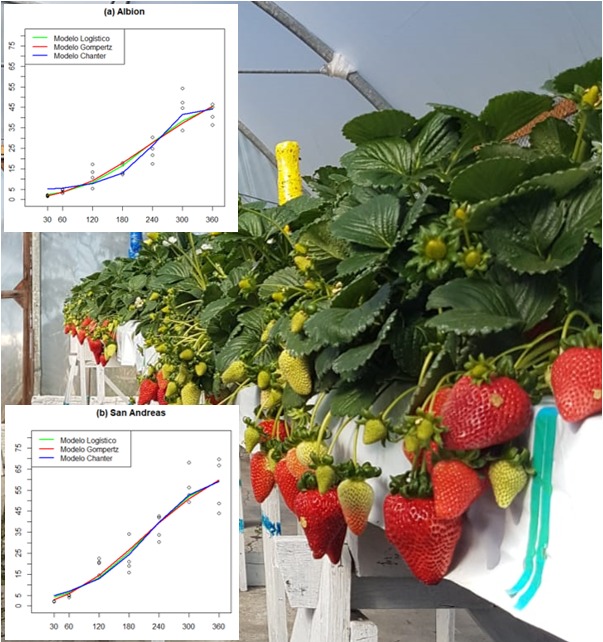
The strawberry plant is a species whose fruits are appreciated worldwide, and the way in which these plants grow and develop has an impact on their productivity and quality. Knowledge about the growth of the plant allows technicians, researchers, and especially producers to master the management of the crop over time, so it is necessary that these growth dynamics be elucidated in scientific studies. The objective of this work was to study the increment of leaf dry mass of two strawberry cultivars during a cultivation cycle, using the classic logistic and Gompertz models, and the Chanter model. The experiment was carried out in a greenhouse, using the Albion and San Andreas cultivars, grown in gutters with substrate, and recirculation of the drained nutrient solution. Seven collections were carried out from March 2022 to March 2023, respectively at 30, 60, 120, 180, 240, 300 and 360 days after planting. Estimates of the model parameters were obtained, two of which had the following practical interpretations: 1 – moment of growth stabilization; 2 - moment of slowdown in growth. Three statistical measures were used to evaluate the goodness of fit of the models: Akaike information criterion (AIC), Bayes information criterion (BIC), and residual standard deviation (SRD). It is concluded that, for the Albion cultivar, the Chanter model presented lower values for the three evaluators, however, for the San Andreas cultivar, the AIC and BIC evaluators indicated the logistic model with the best adjustment, and the DPR indicated the Chanter model.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Proposta de Política para Periódicos de Acesso Livre
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).
