Application of the Detrended Fluctuation Analysis (DFA) method in short or long-range correlations in wind time series of Apodi-RN municipality
Keywords:
DFA, Wind, Statistics, Winds, Time SeriesAbstract
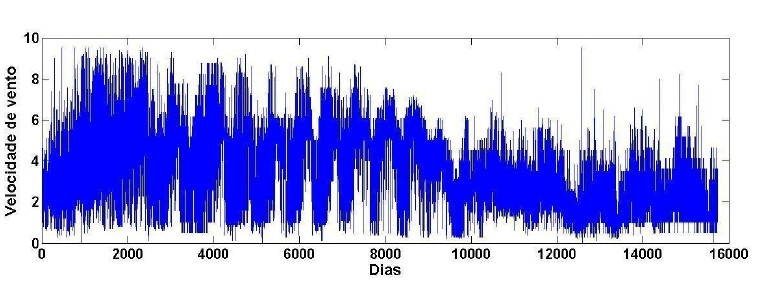
This article aims to investigate short and long-range persistent and anti-persistent correlations in wind time series data from the municipality of Apodi in the state of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. The study employs a statistical method known as Detrended Fluctuation Analysis (DFA) to analyze wind correlations. Renewable energies, particularly wind energy, have been steadily growing as a major energy source used in various countries to power residences, factories, and businesses. Due to its clean, natural attributes and minimal environmental impact compared to other polluting energy sources, wind energy has garnered significant interest from the scientific community. In this context, there is a need to develop technologies capable of assessing wind potential. Statistical methods are employed to analyze wind speed time series, with the objective of quantifying, predicting, and forecasting wind speeds in a specific region. The methodological approach includes a literature review of relevant scientific works, and the DFA application involves three stages: data collection, tabulation, and corrections using software such as R, Geogebra, Excel, among others. The results indicate that wind speed exhibits no anti-persistent correlation or uncorrelated behavior (white noise), but rather persistent correlations, suggesting that high wind speeds are more likely to be followed by high wind speeds.
References
Bezerra, F. H. R., Takeya, M. K., Sousa, M. O. L. 2007. Coseismic reativation of the Samambaia fault, Brazil. Tecnophysics, 430, 27—39.
C.- K. Peng, S. V. Buldyrev, S. Havlin, M. Simons, H. E. Stanley, A. L. Goldberger, Mozaic organization of DNA nucleotides, Physical Review E 49, 1685 -1689, 1994.
criminalidade em Salvador (1980-2000). Dissertação de Mestrado, UNIFACS Universidade de Salvador, 2004.
DOS ANJOS, P. S. et al. Long-term correlations and cross-correlations in wind speed and solar radiation temporal series from Fernando de Noronha Island, Brazil. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, v. 424, p. 90-96, 2015.
ANJOS, Priscilla Sales dos. CORRELAÇÕES DE LONGO ALCANCE EM SÉRIES TEMPORAIS DA VELOCIDADE DO VENTO E RADIAÇÃO SOLAR EM FERNANDO DE NORONHA, BRASIL. 2013. 63 f. Dissertação (Mestrado) - Curso de Biometria e Estatística Aplicada, Universidade Federal Rural de Pernambuco, Recife, 2013.
GONÇALVES, Vanessa Lucas. A bioeletricidade da biomassa residual da cana-de-açúcar e a mudança de paradigma tecnológico no segmento de geração de energia elétrica no brasil. 2016. 84 f. Dissertação (Mestrado) - Curso de Desenvolvimento Econômico, Setor de Ciências Sociais Aplicadas, Universidade Federal do Paraná, Curitiba, 2016. Disponível em: < https://acervodigital.ufpr.br/handle/1884/44168 >. Acesso em: 23 jan. 2024.
Hardstone et al. Detrended fluctuation analysis: a scale-free view on neuronal oscillations, Frontiers in Physiology, November 2012 | Volume 3 | Article 450.
HENRICE JÚNIOR, E. Proposta de utilização do expoente de Hurst da detecção de transientes causados pela fonte externa de nêutrons em reatores ADS. 2017.
HURST, H. E.; BLACK, R. P.; SIMAIKA, Y. M. Long-Term Storage: An Experimental Study. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series A (General), v. 129, n. 4, p. 591-593, 1966.
HURST, Harold Edwin. Long-term storage capacity of reservoirs. Transactions of the American society of civil engineers, v. 116, n. 1, p. 770-799, 1951.
KERDNA PRODUÇÃO EDITORIAL (Brasil) (Ed.). Energia Eólica e Solar. 2018. Disponível em:< http://fontes-de-energia.info/energia-eolica-e-solar.html >. Acesso em: 23 jan. 2024.
LI, Daye; NISHIMURA, Yusaku; MEN, Ming. Why the long-term auto-correlation has not been eliminated by arbitragers: Evidences from NYMEX. Energy Economics, v. 59, p. 167-178, 2016.
LIMA, N. F, FREIRE M. A. C, SANTOS J.J & ALBUQUERQUE R. R. C. Correlação de longo alcance temporal da velocidade do vento nos municípios de Ceará-Mirim e Natal no Rio Grande do Norte; Revisa Holos. 2017. Disponível em www.ifrn.edu.br/ojs/index.php/HOLOS/article/download/5491/ . Acesso em 24 de janeiro de 2018.
MARTINHO, F. M. Energia Eólica: Estudos e Reflexões sobre a viabilidade do potencial dessa matriz energética no Brasil. Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento, Ano 1. Vol. 10 pp. 25-38. ISSN. 2448-0959.
MARTINS, F. R.; GUARNIERI, R. A.; PEREIRA, E. B. O aproveitamento da energia eólica. Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Física, v. 30, p. 1304.1-1304.13, 2008.
MATSOUKAS, A.; ISLAM, S.; RODRIGUEZ-ITURBE, I. Detrended fluctuation analysis of rainfall and streamfall time series, Journal of geophysical research 105, 105 - 129, 2000.
OLIVEIRA NETO, C. R. de; APOLINÁRIO, V. Expansão da energia eólica no brasil, nordeste e rio grande do norte: desafios e oportunidades para o desenvolvimento. In: XX SEMINÁRIO DE PESQUISA DO CCSA, 20., 2015, Natal. Anais... Natal: Não Sei A Editora, 2015. p. 1 - 15. Disponível em: < https://seminario2016.ccsa.ufrn.br/assets//upload/papers/eae5bc76c4b8273c4d926a51a23e245f.pdf>. Acesso em: 23 jan. 2024.
PENA, R. F. A. Fontes renováveis de energia; Brasil Escola. Disponível em http://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/fontes-renovaveis-energia.html . Acesso em 24 de janeiro de 2024.
PENG, C. K. et. al. Long-range correlations in nucleotide sequences, Nature, v.356, n. 6365, p. 168-170, 1992.
SILVA, José Apolinário da. Transformações urbana, socioeconômica e da Study. London: Constable, 1965.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Proposta de Política para Periódicos de Acesso Livre
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).
