Characterization of marked point processes by the marked correlation function
an application to forestry data
Keywords:
Marked Correlation, Marked Point Processes, Spatial Dependence, Kernel EstimatorAbstract
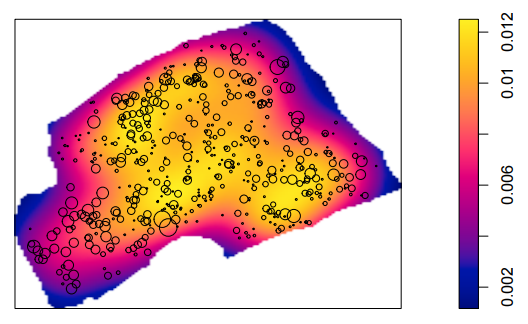
A spatial point process is understood as a set of points (events) irregularly distributed in space, generated by a stochastic probabilistic mechanism. Associating an attribute (mark) with the coordinate determines a marked point process. In the analysis of marked point processes, the interest lies in characterizing the pattern of interaction between the stochastic processes that generated the points and the marks. Analyses start with the characterization of first-order effects for a complete visualization of occurrence intensities. Assuming stationarity, a second-order analysis can be performed to characterize the spatial dependence present in the phenomenon. The data consist of georeferenced locations of occurrence of tree individuals in a native forest fragment and their respective diameters at breast height (DBH). This work aims to characterize the marked point processes by continuous variables, given by the DBH of native trees, through the estimation of the marked correlation function. All analyses were performed using the R software, developed by the R Core Team (2023). From the results, it was possible to observe the potential of the methods used to characterize the patterns and dynamics of the forest under study.
References
BADDELEY, A.; TURNER, R. Spatstat: an r package for analyzing spatial point patterns. Journal of statistical software, 2005. 1-42.
CÂMARA, G.; DAVIS, C.; MONTEIRO, A. M. V. Introdução à Ciência de geoinformação. São José dos Campos: INPE, 2001.
CRESSIE, N. Statistics for Spatial Data. Ames: John Wiley & Sons, 1993.
CRONIE, O.; LIESHOUT, M. N. M. V. A non-model-based approach to bandwidth selection for kernel estimators of spatial intensity functions. Biometrika, 105(2), 2018. 455-462.
DALMASO, C. A. et al. Interações espaciais intraespecíficas de ocotea odorifera na floresta nacional de irati. FLORESTA, v. 46, n. 1, p. 103-114, 2016.
DIGGLE, P. A kernel method for smoothing point process data. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series C (Applied Statistics), 34, 1985. 138-147.
DIGGLE, P. J. Statistical analysis of spatial and spatio-temporal point patterns. [S.l.]:
CRC press, 2013.
DIGGLE, P. J.; RIBEIRO, P. J.; CHRISTENSEN, O. F. An introduction to model-based geostatistics. Spatial Statistics and Computational Methods, 173, 2003. 43-86.
ILLIAN, J. Statistical analysis and modelling of spatial point patterns. Nova York: John Wiley & Sons, v. 70, 2008.
LOADER, C. Local regression and likelihood. Springer Science & Business Media, 2006.
MACHADO, S. d. A. et al. Distribuição espacial de um fragmento de Floresta Ombrófila Mista Montana. [S.l.]: SciELO Brasil, 2012.
MØLLER, J.; WAAGEPETERSEN, R. Some recent developments in statistics for spatial point patterns. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application, Annual Reviews, v. 4, p. 317-342, 2017.
R CORE TEAM. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2023.
SCALON, J. D.; OLIVEIRA, C. A. P. d.; MELLO, J. M. d. Análise espacial de um fragmento florestal baseada no Mosaico de Dirichlet. Revista Árvore, SciELO Brasil, v. 36, p. 733-740, 2012.
SCHAAF, L. B. et al. Alteração na estrutura diamétrica de uma floresta ombrófila mista no período entre 1979 e 2000. Revista árvore, SciELO Brasil, v. 30, p. 283-295, 2006.
STOYAN, D.; PENTTINEN, A. Recent applications of point process methods in forestry statistics. Statistical science, JSTOR, p. 61-78, 2000.
TERRELL, G.; SCOTT, D. Variable kernel density estimation. The Annals of Statistics, 1992. 1236-1265.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Proposta de Política para Periódicos de Acesso Livre
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).
