Sample size for evaluation productive traits of teosinte
Keywords:
Zea mays ssp. mexicana, sample sizing, experimental planningAbstract
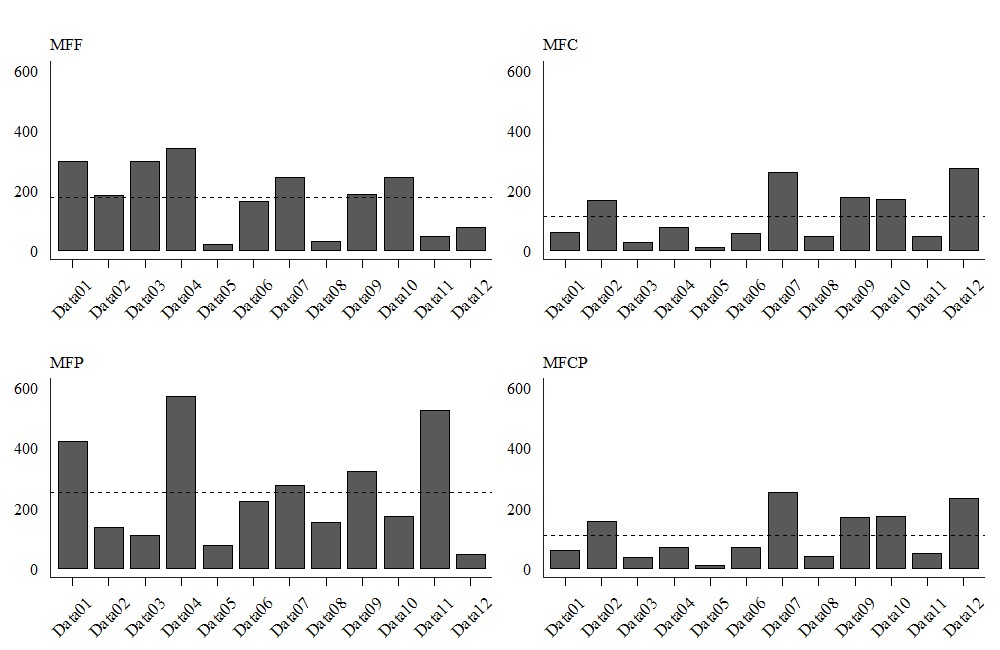
Teosinte (Zea mays ssp. mexicana) is a plant of the Poaceae family and cultivated for the purpose of forage production, pasture and grain. When designing experiments, it is common to ask about the sample size to use to estimate the mean for a given trait. Likewise, the objective of this work was to determine the sample size (number of plants) necessary to evaluate the productive traits of teosinte, in sowing data. An experiment was conducted with 12 sowing dates (10/08/2021, 10/15/2021, 10/23/2021, 10/30/2021, 11/13/2021, 11/20/2021, 11/27/2021, 12/04/2021, 12/11/2021, 12/18/2021, 12/25/2021 and 01/01/2022), in an experimental area located at 29º42'S, 53º49'W and 95m altitude. In the main stem of five plants, chosen at random, for each sowing date, the productive traits were evaluated: fresh mass of main stem leaf (FML), fresh mass of stem main stem (FMS), fresh mass of the main stem tassel (FMT) and fresh mass of main stem (FMMS=FML+FMS+FMT). For each trait the sample size (number of plants) was calculated assuming an estimation error (semi-amplitude of the confidence interval) equal to 10% of the mean estimate, with a confidence level (1- α) of 95%. The sample size for estimating the mean varied between eight plants for FMS (sowing on 11/13/2021) and 573 plants for FMT (sowing on 10/30/2021). The average of the 12 sowings data or sample size were 177, 113, 252 and 109 plants to estimate the average of the traits FML, FMS, FMT and FMMS, respectively.
References
ALVARES, C. A. et al. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, v. 22, n. 6, p. 711-728, 2013.
BALTAZAR, B. M. et al. Pollination between maize and teosinte: an important determinant of gene flow in Mexico. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, v. 110, n. 3, p. 519-526, 2005.
BUSSAB, W. O.; MORETTIN, P. A. Estatística básica. 9.ed. São Paulo: Saraiva, 2017. 554 p.
CARGNELUTTI FILHO, A. et al. Tamanho de amostra para a estimação da média de caracteres morfológicos e produtivos de nabo forrageiro. Ciência Rural, v. 44, n. 2, p. 223-227, 2014.
CARGNELUTTI FILHO, A. et al. Tamanho de amostra para avaliar caracteres produtivos de linho. Agrarian, v. 11, n. 42, p. 387-392, 2018.
DEMPEWOLF, H. et al. Adapting agriculture to climate change: a global initiative to collect, conserve, and use crop wild relatives. Agroecology and Sustainable Food Systems, v. 38, n. 4, p. 369-377, 2014.
FUKUNAGA, K. et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of teosinte. Genetics, v. 169, n. 4, p. 2241-2254, 2005.
GONZÁLEZ, J. J. S. et al. Ecogeography of teosinte. PLoS One, v. 13, n. 2, p. 1-24, 2018.
HUFFORD, M. B. et al. Teosinte as a model system for population and ecological genomics. Trends in Genetics, v. 28, n. 12, p. 606-615, 2012.
KUMAR, B. et al. Herbage production, nutritional composition and quality of teosinte under Fe fertilization. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, v. 18, n. 2, p. 319-329, 2016.
MATSUOKA, Y. et al. A single domestication for maize shown by multilocus microsatellite genotyping. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, v. 99, n. 9, p. 60-80, 2002.
MODOLO, A. J. et al. Sample size determination for maize plants and cob traits under straw management at sowing. Maydica, v. 58, n. 2, p. 151-155, 2013.
R CORE TEAM. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, 2023. URL https://www.R-project.org/.
SANTOS, H. G. et al. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos. 5. ed. Brasília: Embrapa, 2018. 356 p.
TEODORO, P. E. et al. Sample dimension for estimation of biomass and yield of sunn (Crotalaria juncea L.) and showy rattlebox (C. spectabilis Roth.). Journal of Agronomy, v. 14, n. 2, p. 98-101, 2015.
TOEBE, M. et al. Tamanho de amostra para estimação da média e do coeficiente de variação em milho. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, v. 49, n. 11, p. 860-871, 2014.
WANG, L. et al. Kernel amino acid composition and protein content of introgression lines from Zea mays ssp. mexicana into cultivated maize. Journal of Cereal Science, v. 48, n. 2, p. 387-393, 2008.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Proposta de Política para Periódicos de Acesso Livre
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).
