Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on health insurance in southeastern Brazil
an interrupted time series analysis
Keywords:
quasi-experimental models, causal inference, coronavirusAbstract
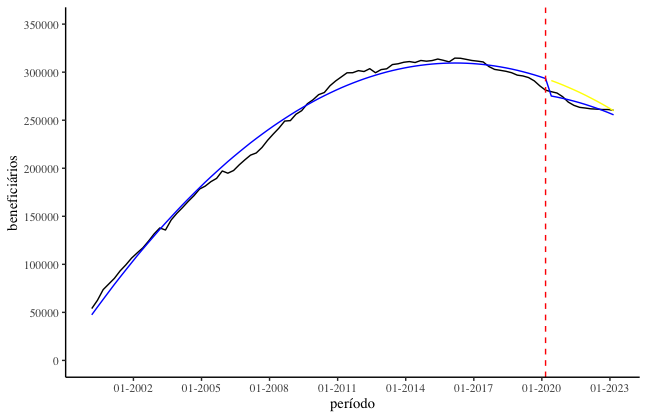
Interrupted time series analysis is the quasi-experimental approach to evaluating the effects of discrete interventions on longitudinal data. Thus, a time series of a given outcome of interest is used to establish an underlying trend, which is "interrupted" by an intervention at a known point in time. The hypothetical scenario in which the intervention did not occur and the trend continues unchanged is referred to as the 'counterfactual'. This counterfactual scenario provides a comparison for evaluating the impact of the intervention by examining any changes that occur in the post-intervention period. In this sense, the aim of this work is to analyze the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on health insurance contracting in the Southeast region of Brazil by means of interrupted series analysis. The data used refers to the number of health insurance beneficiaries in the southeast region from the first quarter of 2000 to the first quarter of 2023 (93 observations), from the National Supplementary Health Agency. Based on the time series analysis, a quadratic model was fitted for the period before the treatment (COVID-19) and after the treatment. Based on the fits of these models, it was possible to observe that the number of health insurance beneficiaries in the southeast was falling, but the intervention may have caused a more pronounced reduction, with an average of 10,000 fewer beneficiaries than predicted without the intervention.
References
BRASIL. Lei no 8.080, de 19 de setembro de 1990. Dispõe sobre as condições para a promoção, proteção e recuperação da saúde, a organização e o funcionamento dos serviços correspondentes e dá outras providências. Disponível em: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/l8080.htm. Acesso em: 30 de Agosto de 2023.
BRASIL. Lei no 9.656, de 03 de junho de 1998. Dispõe sobre os planos e seguros privados de assistência à saúde. Disponível em: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/l9656.htm. Acesso em: 16 de Junho de 2023.
BRASIL. Lei no 9.961, de 28 de janeiro de 2000. Cria a Agência Nacional de Saúde Suplementar – ANS e dá outras providências. Disponível em: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/l9961.htm. Acesso em: 16 de Junho de 2023.
FIGUEIREDO, D. C. M. M. et al. Efeitos da recessão econômica na mortalidade por suicídio no Brasil: análise com séries temporais interrompidas. Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem, v. 75, p. e20210778, 2022.
IRVINE, M. A. et al. An interrupted time-series analysis of pediatric emergency department visits during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Pediatric Emergency Care, v. 37, n. 6, p. 325-328, 2021.
NASCIMENTO, M. I. et al. Mortalidade prematura por câncer de colo uterino: estudo de séries temporais interrompidas. Revista de Saúde Pública, v. 54, 2020.
NUNES, H. R. C et al. Impacto da Lei Seca sobre a mortalidade no trânsito nas Unidades Federativas do Brasil: uma análise de série temporal interrompida. Revista Brasileira de Epidemiologia, v. 24, p. e210045, 2021.
OLIVEIRA, C. C. M. et al. Efetividade do serviço móvel de urgência (Samu): uso de séries temporais interrompidas. Revista de Saúde Pública, v. 53, p. 99, 2019.
PEARL, J. Causal inference. Causality: Objectives and Assessment, PMLR, p. 39–58, 2010.
PENFOLD, R. B.; ZHANG, F. Use of interrupted time series analysis in evaluating health care quality improvements. Academic pediatrics, v. 13, n. 6, p. S38-S44, 2013.
RUBIN, D. B. Estimating causal effects of treatments in randomized and nonrandomized studies. Journal of educational Psychology, American Psychological Association, v. 66, n. 5, p. 688, 1974.
ROSENBAUM, P. R.; RUBIN, D. B. The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects. Biometrika, Oxford University Press, v. 70, n. 1, p. 41–55, 1983.
VINCI, A. et al. Emergency medical services calls analysis for trend prediction during epidemic outbreaks: interrupted time series analysis on 2020–2021 COVID-19 epidemic in Lazio, Italy. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, v. 19, n. 10, p. 5951, 2022.
Downloads
Published
Versions
- 11-04-2024 (2)
- 15-03-2024 (1)
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Proposta de Política para Periódicos de Acesso Livre
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).
